As a first-line treatment, NovoSeven® RT is 95% effective and recommended by an international consensus.a,b
Proven to be effective.
aInternational consensus based on research from Tiede A, Collins P, Knobeln P, et al. International recommendations on the diagnosis and treatment of acquired hemophilia A. Haematologica. 2020;105:1-44.
bEfficacy was assessed in 103 bleeding episodes in a review of 139 patients with acquired hemophilia.
Made without human blood or plasma
Recombinant manufacturing means NovoSeven® RT is made without any human blood or plasma, which minimizes the possibility of viral contamination.

Lower volume means fast infusion.
Because it's a low-volume treatment, NovoSeven® RT takes 2 to 5 minutes to infuse.b
bAdminister as a slow bolus injection over 2 to 5 minutes, depending on the dose administered.
Volume

Infusion time
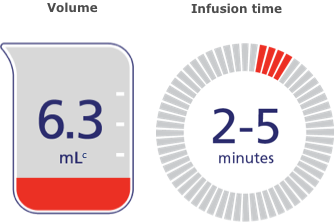
cBased on the initial dose for a 70-kg patient with acute bleeding.
What if I need surgery or a procedure?
We understand that you have concerns about controlling bleeds if you ever need surgery or a procedure. The good news is that NovoSeven® RT is effective for preventing bleeds during and after surgery and procedures in people with acquired hemophilia.
Talk to your doctor for more information on the surgical use of NovoSeven® RT.
About acquired hemophilia (AH).

What is acquired hemophilia?

Acquired hemophilia is a bleeding disorder that prevents blood from clotting properly. Unlike congenital hemophilia, which is an inherited disorder, acquired hemophilia is not present at birth; it develops suddenly. When a person develops acquired hemophilia:
- Their body develops antibodies, or "inhibitors," that fight its own blood-clotting factors, mostly factor VIII
- Spontaneous, uncontrolled bleeding can occur

Who gets acquired hemophilia?

Acquired hemophilia occurs in people with no personal or family history of bleeding disorders. It is very rare, occurring in only about 1 to 1.5 per million people each year. It usually affects older people, as well as women who have recently given birth.
Acquired hemophilia can occur in association with other underlying conditions that involve the immune system, like cancer, other autoimmune diseases, or pregnancy. In about half of cases, there is no clear medical condition or reason that it happens.

What are the symptoms of acquired hemophilia?

Acquired hemophilia can happen without warning. The most common symptoms are:
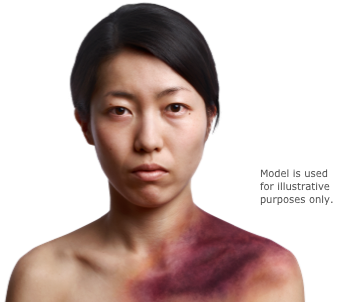
- Bleeding into the skin (bruising)
- Bleeding into soft tissues
- Internal bleeding
- Excessive bleeding following childbirth or surgery
Acquired hemophilia is diagnosed with laboratory tests that measure clotting time of blood and factor VIII levels.


Hear from people who
share your experience.

New to treatment? It’s
easy to get started.
![Icon: 5-step purification process of NovoSeven® RT (Coagulation Factor VIIa [Recombinant])](/content/dam/novonordisk/novoseven/cta/CTA-recombinant.jpg)
![NovoSeven® RT (Coagulation Factor VIIa [Recombinant])](/content/dam/novonordisk/novoseven/global/logo-novoseven-rt.png)